Common Average Reference#
Plugin Type |
Filter |
Platforms |
Windows, Linux, macOS |
Built in? |
Yes |
Key Developers |
Ryan Maloney, Josh Siegle, Kirill Abramov |
Source Code |
Tip
If you’re using Neuropixels probes, the Neuropixels CAR plugin will be more effective at removing noise.
Overview#
Common average referencing is a widely used technique for removing noise from extracellular recordings. Since artifacts often originate from sources that are distant from the electrodes, they induce similar voltage fluctuations across all channels. Thus, computing the average value of some or all channels, and then subtracting this from the incoming data, can help isolate the signals that are generated locally.
This plugin can be used for common average referencing across any number of channels, or it can perform simple digital referencing by selecting a single channel as the reference. If different subsets of electrodes are differentially affected by noise sources, multiple common average reference plugins can be used.
Note
It’s recommended to place this plugin after the first Record Node in your signal chain, so the data is saved without referencing applied. Global referencing can be easily performed offline, for example by using a common median reference that is less sensitive to outliers (but is more computationally intensive than averaging).
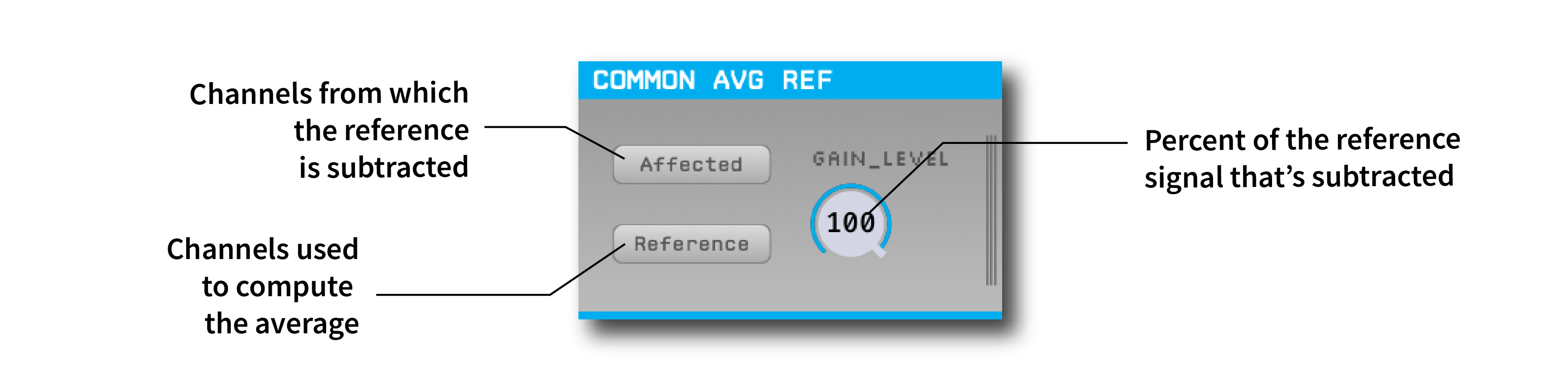
Plugin configuration#
There are three settings that affect the behavior of the Common Average Reference:
Affected channels: These are the channels to which the referencing is applied.Reference channels: These are the channels which are averaged to compute the reference signal. To implement simple digital reference to one electrode, select a single channel at a time.Gain level: The percentage of the reference signal to use. For a gain level of 100%, the reference signal will be multiplied by 1.0. To adjust the gain level, click on the gain slider and drag upwards or downward.
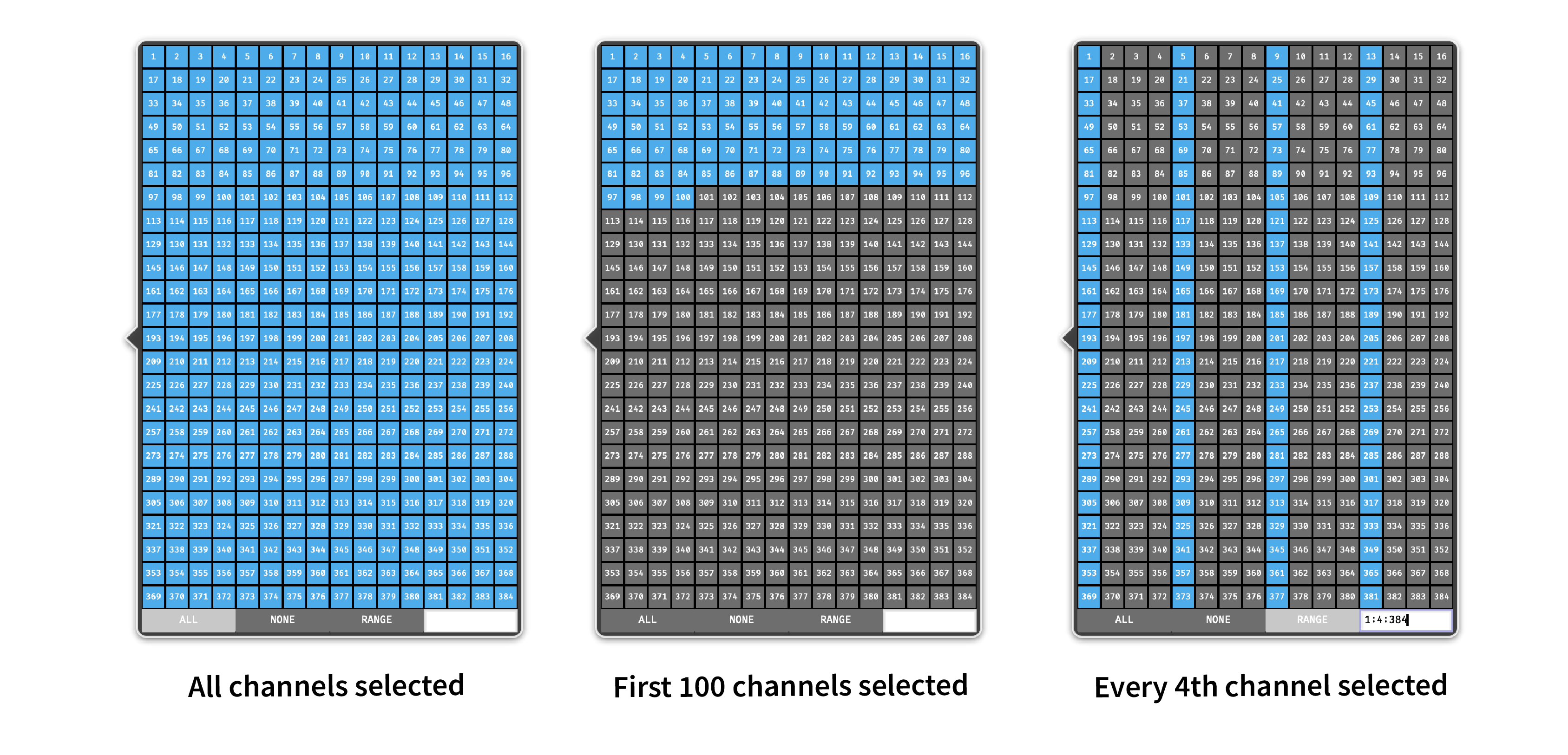
Some example channel configurations are illustrated in the figure below:
Working with multiple data streams#
The “Reference” and “Affected” channels are only applied within a single stream. Because different streams may be sampled asynchronously, it’s not possible to reference channels from one stream to channels in another.
To change the settings for a particular stream, make sure it is active in the stream selector (accessed by clicking the vertical lines on the right-hand side of the plugin editor).